Our Specialities
- Introduction
- Causes of Damage
- Possible Post Operative Complications
- Complications After Hip Surgery
- Before Your Operation
- Peri-Operative Protocol
- Physiotherapy
Hip Replacement
Introduction
The hip joint comprises of a long thigh bone articulated with cup shaped cavity of hip bone.Rounded head of the thigh bone fits into the cavity to from a ball and socket joint.
The surface of the head of the thigh bone and the socket are covered by specialised tissue called articular cartilage.The joint cavity is lined by a membrane called the synovium which secretes synovial fluid into the joint and allows smooth movement of the ball within the socket.
Prosthesis Of Hip Joint :
The doctor will decide about the best material to be used in your particular case. This selection will depend upon factors such as –
- You’re age
- Normal level of Activity
- Degree of damage
- Deterioration of bones of your Hip Joint
Although a replaced hip joint may continue to function successfully for 15 yrs. or more, it will not last forever. Careful consideration is therefore necessary before replacing the hip of someone in their forties or fifties, as they are likely to require revision surgery in future. In such conditions cementless prosthesis may be most appropriate.
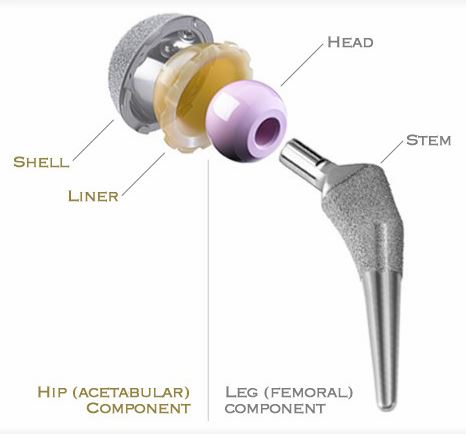
Femoral Component :
Femoral component prosthesis replace the head of the femur. It contains ball shaped head & a stem which is inserted into the shaft of femur.
Femoral component is made of a variety of metals
Stem :
Cemented Stem :
Cemented Stem is made from steel, titanium & titanium alloys and is highly polished. It is fixed with the help of cement in femoral shaft.
Uncemented Stem:
Uncemented Stem is coated with Hydroxyapatite or is porous coated. It fixes into femoral shaft. These allow bone to grow onto their surface.
Head :
Head is fixed on neck of stem & acetabulum component. It is made of any one of the following metals. –
Cobalt Chrome it's miles a completely sturdy alloy having excessive resistance to wear & corrosion.
Oxidized Zirconium
It is toughest metal known today. It is also having high resistance to wear & corrosion.
Ceramic :
Ceramic cornponents are brittle but hard which do not scatter easily, are durable & have low friction. These are particularly good in young active people.
Acetabular component :
Uncemented :
IUncemented : It consists of a shell & a liner. The shell is made of titanium alloy, which allow bone to grow easily onto its surface. These have good press fit design. The liner is made of highly cross linked polyethylene and has very good wear properties.
Ceramic liners are also available, and are durable & have low friction.
Cemented :
Cemented components are manufactured from rather pass connected polyethylene and have superb wear residences.
Hip Replacement
Causes of Damage
There are several illnesses which could harm the knee or hip joint in addition to different joints of the body also. these diseases motive damage to the surfaces of the bones taking element inside the joint formation ensuing in intense ache and incapacity.
Osteoarthritis :
Osteoarthritis is the most common cause for destruction of most of the joints of the body including the knee & hip joint. As the age progresses the cartilages over the ends of bones degenerate due to friction caused by the use of the joint. Once the cartilage is lost the surface of the bones beneath gets exposed. Due to the continuous rubbing and friction while walking the surface of the bone gets worsened and the individual cannot take even a single step without pain. Osteophytes formed at the margins of the joint restrict the movement of the joint. Due to severe pain and destruction of the joint one may start limping while walking and that will cause problems to the spine. For management of osteoarthritis one may use cane for support while walking, physiotherapy and take pain killer tablets or intra- articular injections.
Rheumatoid Arthritis :
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease of connective tissues which involves inflammation of several joints. It starts in early age and can affect both men and women, more often women. The affected joints become swollen and tender. The bones become demineralised and muscles weak and atrophied.
The cause of all types of osteoarthritis is not always known.Some people suffer from haemophilia which is a bleeding disorder in which repeated bleeding into the joint results in swelling and inflammation, with subsequent destruction of the articular cartilage. Infection of the joint , accidental injury, gout, death of the tissue of the bone due to alcoholism, long term use of steroids or pain killers are some of the known causes. Some people suffer from dislocation of the hip joint right from birth which puts pressure on the joint causing excessive wear and tear of the joint.
Hip Replacement
Possible Post Operative Complications
These are some common complications associated with each type of surgery & some are specifically related to hip replacement surgery. Most complications are minor but it is important to be aware & to seek medical attention.
Chest Infection
Possible following general anaesthesia and particularly in smokers.
Deep breathing is important
Fever
It can develop in the first 24-72 Hrs.after surgery.Its cause will have to be investigated and treated accordingly.
Thrombosis & Embolism
After surgery blood clot (deep vein thrombosis) may occur in one of the deep veins of the body.
We take precautions to prevent this from happening.
1.Wearing Anti-Embolism stockings : at least for 6 weeks.
2.Course of blood thiner Injections/Tablets.
3. Exercises & Early Mobilization after surgery.
Infection
It is always a risk when materials are implanted into the body.
We use special precautions to avoid this
1.Operation theaters with laminar flow.
2. Operating Staff with disposable suits. (Space Suits)
3. Antibiotics in peri operative period.
Sepsis
Sepsis may be caused by pus producing organisms. Main cause is contamination of the wound
You need to take proper medical advice if you have pain, swelling, heat and redness around wound or with leakage of pus and high fever.
Nerve damage
The small nerves supplying the skin over operation site are usually damaged. When an incision is made during surgery it can cause numbness around wound. This does not in any way affect the function following surgery
Hip Replacement
Complications After Hip Surgery
Apart from above complications following complications are specifically related to hip replacement surgery –
Dislocation
It involves complete displacement of the head of the femur from acetabulum. It is not common complication.
Patient needs to take precautions as advised by the surgeon.
Aseptic Loosening
Most common cause of component failure may be because of poor quality bone, excessive body weight, improper or excessive activity.
Fracture of femur around an implanted stem is a serious complication. Sometimes implant loosening associated with osteolysis weakens bone stock & may predispose to fracture.
Hip Replacement
Before Your Operation
After your decision to go in for a joint replacement you should be aware of the basic things to be done before surgery. Such as –
- Suitable prosthesis for you.
- The cost of your prosthesis.
- Total Hospital stay & cost of hospital stay.
- The Blood, Heart and Chest investigations.
- Get this investigations 2-3 weeks before the date of surgery & get them checked by a physician.
- It is necessary to confirm that there is no active infection in your body.
- If you have mediclaim facility, you should contact hospital’s mediclaim department at least one week before surgery with your policy documents.
- You should show the drugs which you are already taking. Some types of medicines like steroids & blood thinning medicines are to be stopped 5-7 days prior to surgery.
- For admission in hospital take admission letter from your surgeon.
- You may advised to get admitted 1-2 days prior to the surgery. Take all investigations report, previous medical records & drugs with you.
Hip Replacement
Peri-Operative Protocol
After Admission:
After you are admitted in the hospital, a resident / registrar doctor will come to you. He will examine you again & explain you in brief things to be carried out before & after the operation. A physician will come & examine you & will give the fitness for surgery.
Anaesthetist visit:
Anaesthetist will come to you & will examine you from the view of anesthesia. He will explain to you in brief the type of anaesthesia, drugs to be stopped & the drugs to be taken on the day of surgery. You will be asked to stop taking food or drinks at least 6 – 8 hrs. before surgery.
Anaesthesia
Anaesthesia will be spinal & epidural in which the lower part of your body will be anaesthetized. You will be awake during surgery. A thin plastic tube will be inserted into your back through which anaesthetic drug along with pain killers will be induced in your body. Because of this you will feel numbress in your legs. This tube may kept in your back for couple of days for pain relief.
Bathing
You will be asked to have bath on the previous night of surgery & a couple of hours before surgery, to maintain cleanliness of your body & operation site.
After Your Operation:
After surgery you will be kept in the recovery room for couple of hours. After that you will be shifted to your room. You will be asked to keep fasting for 4-6 hrs. after surgery. After that you can start orally with clear liquids first. If there is no vomiting, you can have a light diet on the night of surgery.
Drips
There may be an intravenous drip for next 2 – 3 days for admission of antibiotics, saline & fluids. Once you will start taking food orally, saline & fluids will be discontinued but antibiotics will be continued for the next couple of days.
Wound Drains:
There may be one or more small plastic tubes extending out of the side of the wound dressing, draining into a bottle. These tubes enable excess fiuid & blood to drain away from the wound. Dressing will be checked & changed as required. Pillow will be given under calf to avoid pressure sores.
Simple Exercises:
You are advised to do some simple exercise before & after operation. You should start them as soon as possible when you are still in recovery room or shifted to your room.
Deep Breathing
– Deep breathing and coughing will help to keep your lungs supplied with oxygen & clear the sputum.Leg Execises
– Simple leg exercises will help to reduce risk of deep vein thrombosis & can easily be done. Some of them will also help mobilize your hip joint & strengthen your muscles.Foot Flexion & extension & circular movements.
Lying on your back, press your kness on to the bed with your leg straight.
Pain Relief :
If you have had an epidural anaesthesia, pain killer drug may be infused through it.
After first couple of post operative days, regular pain killers will probably provide sufficient pain relief, likely to be continued for several weeks to enable you to do necessary exercises.
In hospital, if your pain is not being controlled kindly inform a doctor or nurse, as it may be possible to give you stronger pain killers.
Thrombosis Prevention :
Blood clots are most common about 2 days after surgery. Although they can develop any time upto 3 weeks later.
Prevention – –Daily injection of low dose anti-coagulant or tablet until you are in hospital.
You will be asked to wear anti-embolism stockings for upto 6 weeks after surgery.
Blood Test :
A sample of your blood will be taken to measure hemoglobin level. If hemoglobin is low –
May be started on iron tablets.
Sometimes blood trans fusions are required.
X-RAYS :
An x-ray will be taken of your operated joint, either in the recovery room or within 48 hrs. after operation.
Bladder Function :
You will have a urinary catheter that will drain your urine from your urinary bladder. It will kept there for the next 3-4 days until you are able to urinate voluntarily in a bed pan or commode-chair near bedside.
Hip Replacement
Physiotherapy
Car Transfer :
Getting into a car :
- Be sure the passenger seat is pushed all the way back.
- Recline the seat back as far as possible.
- With your walker in front of you, slowly back up to the car seat.
- Sit on the car seat.
- Swing your legs into the car.
- When traveling make frequent stops and get out & walk around.
Getting out of car :
- Push the seat all the way back.
- Recline the seat all the way back.
- Lift your legs out. Place the walker up in front of you & stand up on the unaffected leg or leg which is having less pain.
Climbing up stairs
- Use a hand rail ( if available ) to climb stairs.
- Lead with your non-operated leg or less painful leg, then operated leg and finally your crutches or cane.
- A family member should stay one step below helping you to climb stairs.
Going down stairs
- Use a hand rail ( if available ) to go down stairs.
- Lead with your crutch or cane, then your operated leg and finally non- operated or less painful leg.
- A family member should stay one step below, helping you to go down stairs.
Chair Transfer :
- Back up to the chair until you feel both legs touching the chair.
- Slide your operated leg out in front of you, place one hand on the armrest.
- Lower your self slowly, keeping your operated leg straight out.
- When getting up, scoot your operated leg out in front of you until you can stand on it comfortably.
- Push up using the armrests, keeping your operated leg out in front of you.
Bed Transfer
Getting up
- Pivot to your hips the usage of your elbows to assist. hold your frame instantly with your operated
- leg saved to the aspect. Do no longer twist your legs.
- pass your unoperated leg around & take a seat on the edge of the bed maintaining your operated leg straight. hold on for your walker for guide and stand.
Getting back in bed
- Stand near the bed with your lower back to it.
- Stand near the bed with your back to it.
- Lower your body until you are sitting on the edge of the bed with your operated leg straight out in front of you.
- Swivel on your bottom & lift your unoperated leg into the bed first, followed by your operated one.
toilet
- Put one hand on the wall, wash basin handrail for support.
- Keep operated leg straight in front of you. Reach down to put your other hand on to the toilet seat.
- Lower yourself onto the seat.
- To stand from the toilet, reverse this procedure.
Walking
- A physiotherapist will help you to walk a short distance with walker.
- After couple of days, you may be able to progress to walking with a walker independently.
Precautions to be taken after Hip Replacement
- Don’t cross your legs.
- Don’t sit on a low chair. Height of your Hip joint should always be higher than height (level) of your knee joint.
- Don’t sit with legs crossed.
- Don’t sit on the floor
- Don’t use Indian style toilet, use commode
- Avoid twisting & bending forwards.
